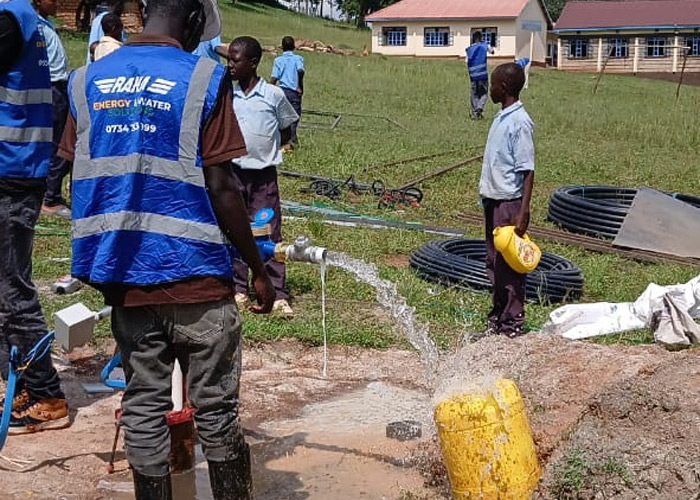
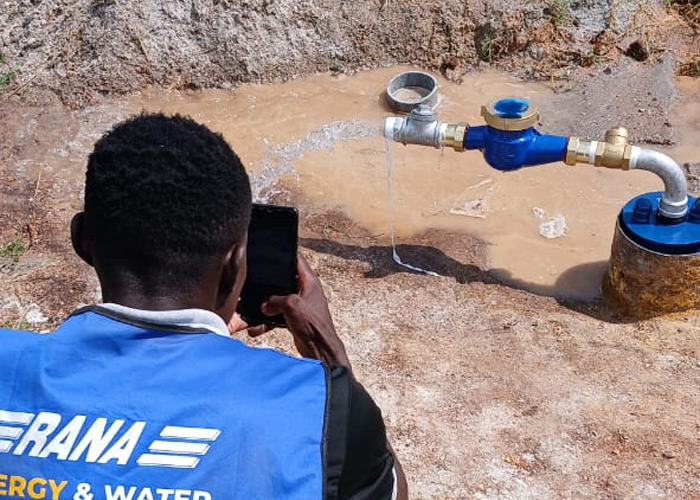








Test Pumping
Borehole pump testing is a crucial process of controlled water extraction to determine a borehole’s sustainable yield (flow rate), aquifer properties, and optimal pump size by monitoring water level drawdown and recovery over time, preventing over-pumping and ensuring efficient, long-term water supply for various uses like domestic, agricultural, or industrial needs. Key tests include Step-Drawdown (varying rates to find optimal performance) and Constant Discharge (long-term pumping for yield) followed by a recovery test.
Key Details of Test Pumping
*Why it's Done *
Determine Yield: Find the maximum sustainable water flow rate.
Select Pump: Guide the choice of the right pump to avoid damage (silting, burnout) from over or under-pumping.
Aquifer Assessment:
Understand aquifer characteristics, boundaries, and response to pumping.
Water Quality:
Check for changes in water quality during continuous use.
Licensing:
Provide data for regulatory compliance.
Key Types of Tests: Step-Drawdown Test:
Pump at increasing, fixed rates (steps) for short periods (e.g., 15-60 mins each).
Measures drawdown at each step to identify efficient operating points.
Constant Rate (Yield) Test:
Pump at a steady, controlled rate for an extended period (24-72 hours).
Monitors drawdown to find the sustainable yield.
Recovery Test:
After pumping, stop and monitor how quickly the water level returns to its static level.
What's Measured & How
Pumping Rate : Measured with flow meters.
Water Level (Drawdown): Measured using dip meters (electric probes on tapes) or data loggers in the borehole and nearby observation wells.
Time: Readings taken at precise intervals.
Importance
Prevents Well Failure: Avoids damaging the aquifer or well structure.
Ensures Efficiency : Matches pump to well capacity.
Data-Driven Decisions : Provides reliable data for long-term water management.
